OASIS: Orbital Antimatter Synthesis & Injection Station
Patent Pending
GreyArray Skunk Works | Published:
Introduction
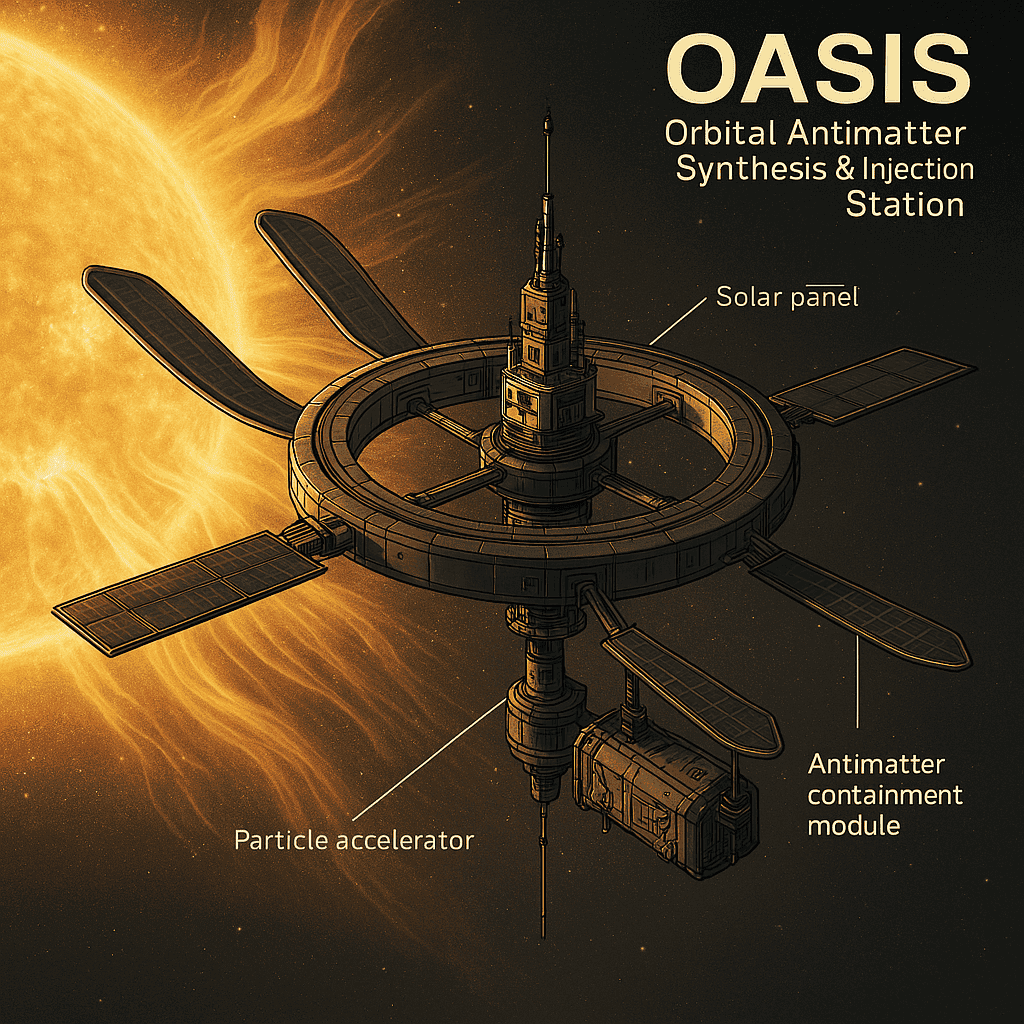 In the realm of futuristic energy systems, few concepts are as powerful and elusive as antimatter. Long imagined in science fiction and theoretical physics alike, antimatter holds the promise of nearly incomprehensible energy densities. The challenges, however, have always been formidable: creation, containment, and utility. With the unveiling of OASIS — the Orbital Antimatter Synthesis & Injection Station — these challenges are no longer the realm of the impossible. OASIS proposes a bold, practical design for harvesting antimatter directly from space, converting cosmic radiation into usable stored energy.
In the realm of futuristic energy systems, few concepts are as powerful and elusive as antimatter. Long imagined in science fiction and theoretical physics alike, antimatter holds the promise of nearly incomprehensible energy densities. The challenges, however, have always been formidable: creation, containment, and utility. With the unveiling of OASIS — the Orbital Antimatter Synthesis & Injection Station — these challenges are no longer the realm of the impossible. OASIS proposes a bold, practical design for harvesting antimatter directly from space, converting cosmic radiation into usable stored energy.
Developed as part of GreyArray’s advanced skunk works initiative, OASIS is an orbital platform engineered to collect high-energy solar wind particles, synthesize antimatter in situ, and securely store it for future use. With autonomous management systems and precision containment technologies, OASIS could become the cornerstone of a new energy paradigm.
The Need for Antimatter Energy
Antimatter is the mirror opposite of normal matter: for every particle, such as a proton or electron, there exists an antiparticle — the antiproton and the positron. When matter and antimatter collide, they annihilate with near-total efficiency, releasing pure energy according to Einstein’s E=mc². No chemical or nuclear process known today can match the energy potential of antimatter.
Despite its promise, antimatter is almost entirely absent in our observable universe and is exceedingly difficult and expensive to create using current Earth-based particle accelerators. The energy cost to produce even a single gram of antimatter is astronomical. Traditional methods are simply not scalable. What’s needed is a system that can bypass Earth’s limitations and operate in the most particle-rich environment available: space.
This is the problem that OASIS was designed to solve.
The Vision of OASIS
OASIS exists to perform the three most difficult tasks in antimatter development — collection, synthesis, and containment — in one elegant, autonomous orbital system. Its design is both modular and scalable, allowing for deployment across multiple orbits and integration into broader interplanetary infrastructure.
At its core, OASIS is not just a technological platform; it is a vision of how humanity can learn to harness the chaotic brilliance of the cosmos. By turning our solar system’s natural particle flux into the raw ingredients for antimatter, OASIS enables a future of propulsion and power that transcends the constraints of fuel-based energy systems.
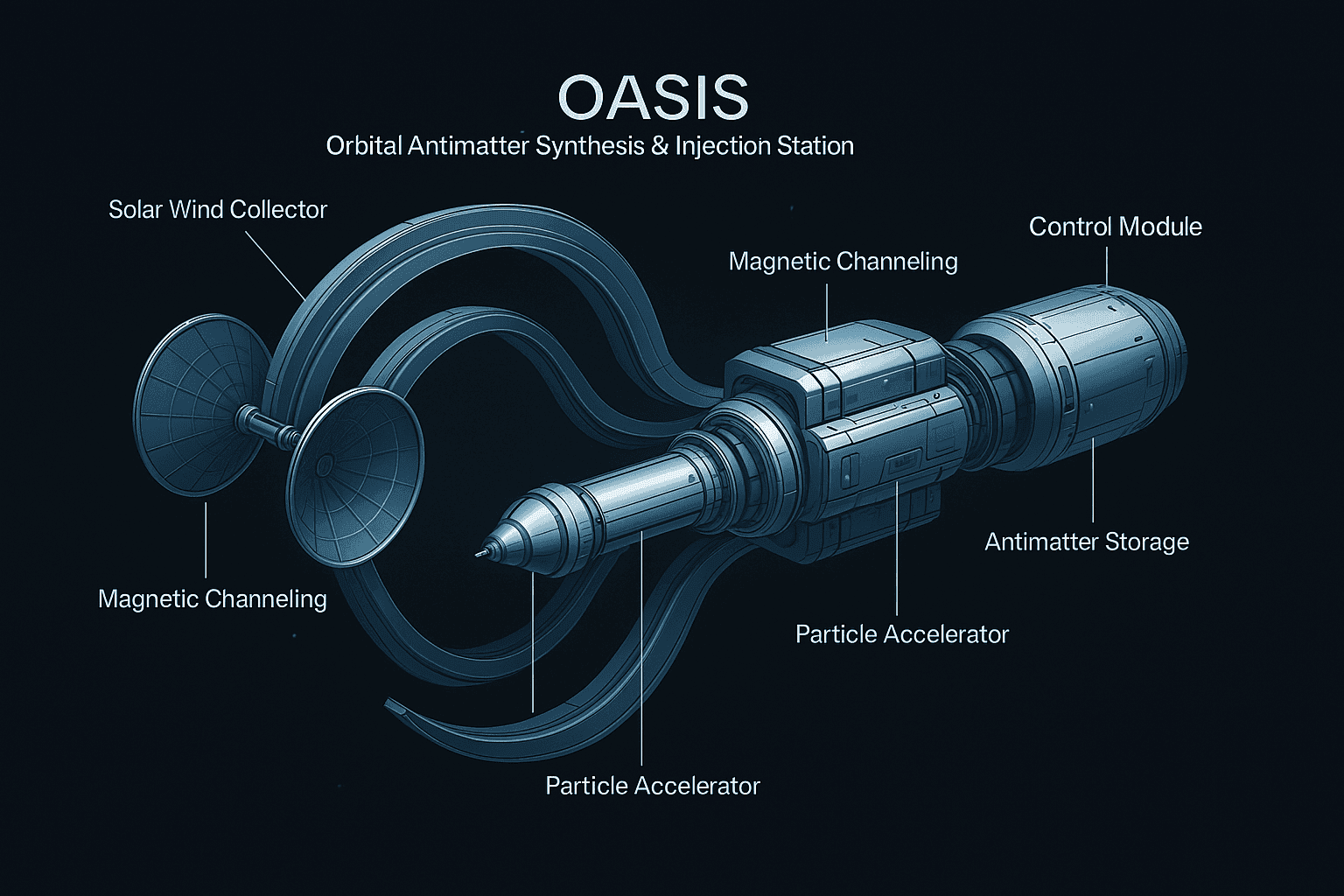
Core Components
1. Magnetic Particle Collection Array
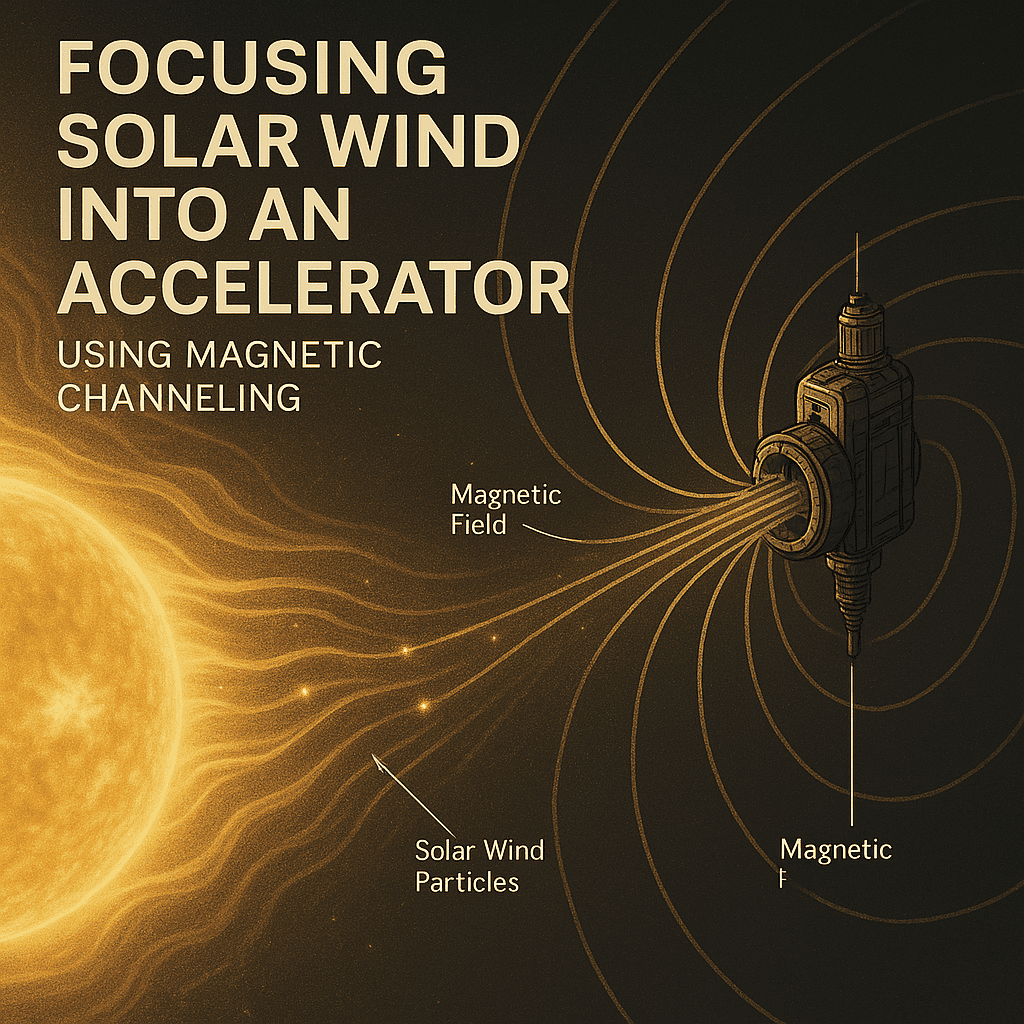 Solar wind is composed primarily of protons and electrons moving at high velocities, bombarding space-based systems continuously. OASIS uses a proprietary magnetic collection array to channel these particles into its core systems. The array functions like a net, gathering and compressing particle streams without physical contact, relying instead on dynamically modulated electromagnetic fields.
Solar wind is composed primarily of protons and electrons moving at high velocities, bombarding space-based systems continuously. OASIS uses a proprietary magnetic collection array to channel these particles into its core systems. The array functions like a net, gathering and compressing particle streams without physical contact, relying instead on dynamically modulated electromagnetic fields.
2. Antimatter Synthesis Core
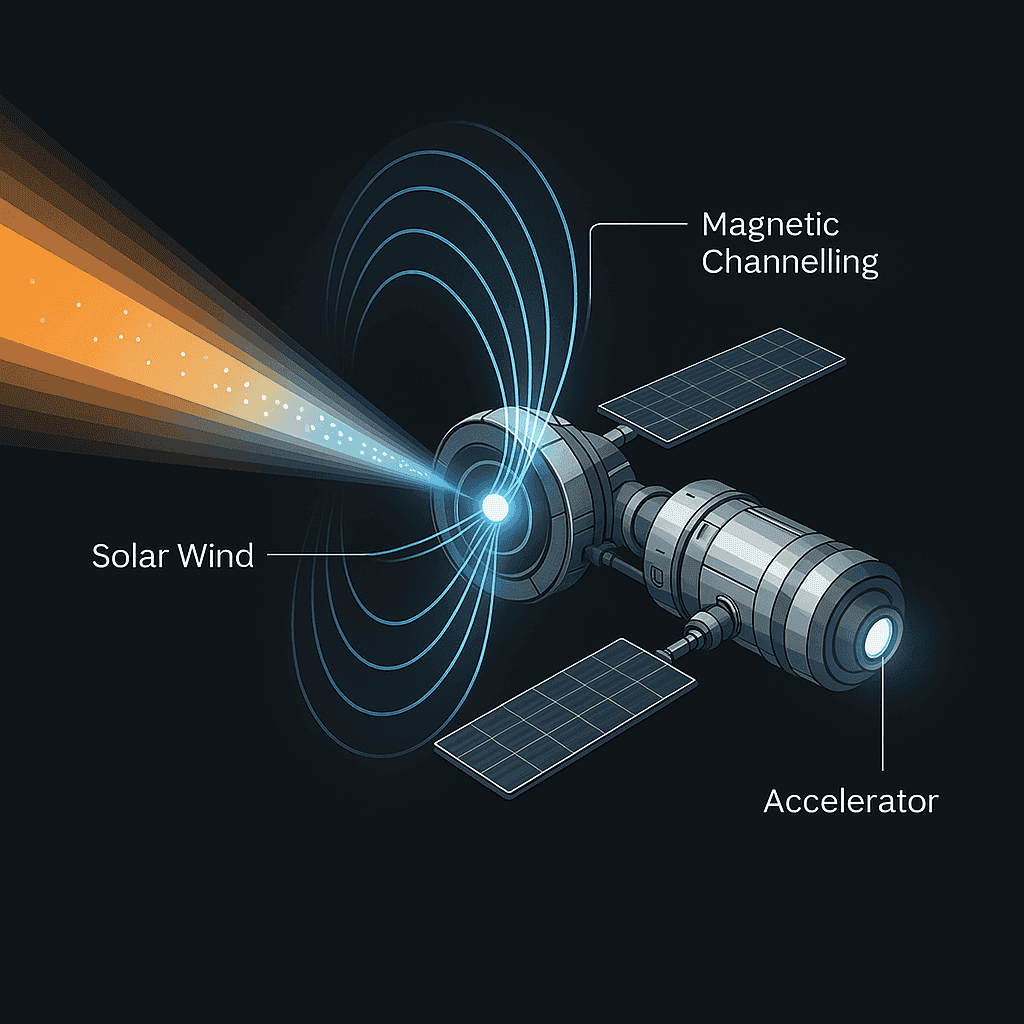 Within a vacuum-sealed, radiation-hardened chamber, collected particles are accelerated and collided at precisely calculated energies. These collisions produce high-energy interactions capable of generating antiparticles — particularly positrons and antiprotons. The synthesis core operates under constant modulation, adjusting for solar intensity, particle composition, and energy flux.
Within a vacuum-sealed, radiation-hardened chamber, collected particles are accelerated and collided at precisely calculated energies. These collisions produce high-energy interactions capable of generating antiparticles — particularly positrons and antiprotons. The synthesis core operates under constant modulation, adjusting for solar intensity, particle composition, and energy flux.
3. Containment and Storage Architecture
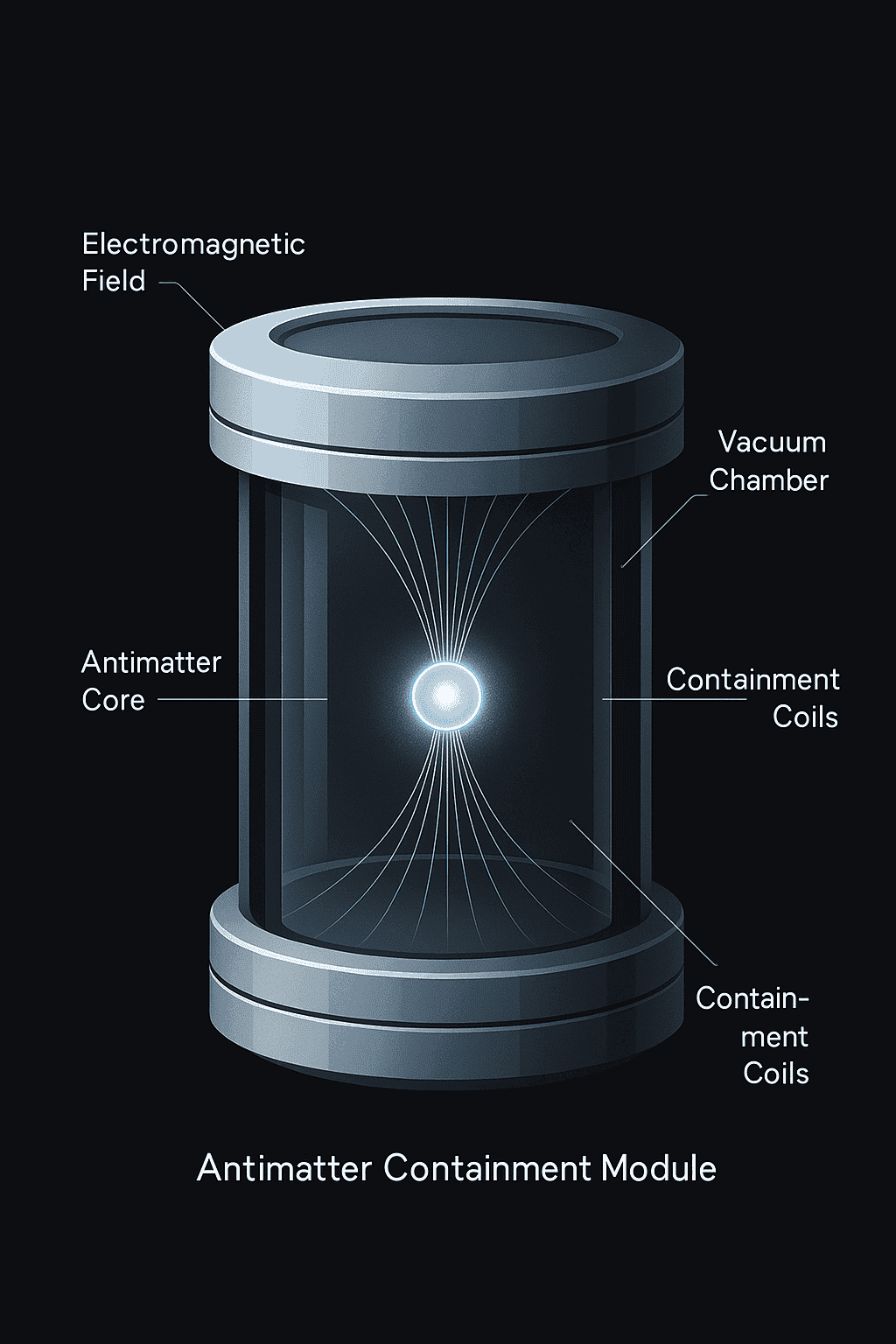 The most challenging aspect of antimatter management is containment. OASIS employs advanced Penning and Paul trap configurations to isolate antimatter within ultra-stable electromagnetic bottles. These traps are housed in vacuum-insulated compartments to prevent annihilation reactions and are suspended in gimbal-stabilized enclosures to resist orbital vibration or micrometeoroid impacts.
The most challenging aspect of antimatter management is containment. OASIS employs advanced Penning and Paul trap configurations to isolate antimatter within ultra-stable electromagnetic bottles. These traps are housed in vacuum-insulated compartments to prevent annihilation reactions and are suspended in gimbal-stabilized enclosures to resist orbital vibration or micrometeoroid impacts.
Safety is paramount. In the event of power fluctuation, orbital drift, or trap degradation, redundant containment layers are activated and antimatter quantities are immediately isolated or ejected in controlled micro-capsules.
4. Autonomous AI Governance System
To operate continuously in the volatile environment of space, OASIS is equipped with an onboard AI that manages all platform systems. This AI evaluates solar particle density, orbits, containment stability, energy storage thresholds, and docking readiness. It can execute adaptive behavior such as shifting orientation for better solar exposure or particle intake, adjusting field strengths in real-time, and activating defensive protocols against solar flares.
Scientific and Engineering Challenges
- Magnetic Precision: The collection and synthesis processes require micro-level magnetic field adjustments to stabilize and target particles.
- Energy Management: Solar panel arrays, thermal regulation fins, and onboard capacitors must maintain the power flow needed to sustain traps and synthesis operations.
- Shielding and Materials: Exposure to solar radiation and high-energy particles necessitates robust shielding using layered carbon composites and adaptive mesh materials.
- Redundancy and Recovery: All systems are designed for fault tolerance, with triple-redundant logic systems and manual override sequences available via secure uplink.
Future Applications
- Interplanetary Propulsion: Antimatter fuel could allow spacecraft to achieve delta-v velocities far beyond current chemical or ion engines.
- Orbital Power Storage: Energy collected and stored in antimatter form could be converted and dispatched with near-instantaneous effect.
- Emergency Burst Power: In orbital or lunar settings, antimatter could serve as an emergency backup source for recharging habitats, defense shields, or launch platforms.
- Scientific Discovery: An orbital antimatter lab offers a testbed for exploring exotic physics, quantum particle behavior, and novel energy conversion systems.
Conclusion
 OASIS is not just an engineering project — it’s a reimagining of how energy can be captured, created, and wielded. By moving antimatter generation into space, we sidestep the constraints of gravity, atmosphere, and infrastructure, and instead tap into the raw streams of cosmic energy flowing through our solar system.
OASIS is not just an engineering project — it’s a reimagining of how energy can be captured, created, and wielded. By moving antimatter generation into space, we sidestep the constraints of gravity, atmosphere, and infrastructure, and instead tap into the raw streams of cosmic energy flowing through our solar system.
As a concept and as a working design, OASIS represents the kind of thinking that defines GreyArray: bold, high-risk, high-reward experimentation designed to push the boundaries of what is physically and imaginatively possible. This platform is a declaration — that we are no longer just observers of the cosmos, but active participants in shaping the energy systems of the stars.